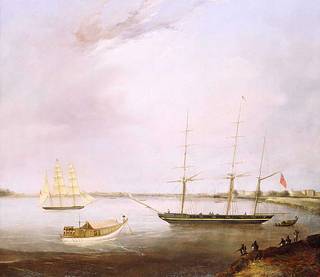
Similar
The 'Streatham' and the opium clipper 'Red Rover' RMG BHC3580
Summary
The 'Streatham' and the opium clipper 'Red Rover'
The ‘Streatham’ with the opium clipper ‘Red Rover’ are shown at anchor in the Hooghly River, Calcutta. The buildings of Calcutta dominate the skyline in the background. A local craft with passengers seen through the louvred canopy is being rowed from the ‘Streatham’. Figures on the shore on the right survey the scene and the nearest man appears to be fishing in the mighty river. Two thirds of the painting is sky which emphasises the vast scale of India.
The ‘Streatham’ was a ship of the Honourable East India Company. The ‘Red Rover’ was the first and most famous of the purpose-built 'opium clippers' which carried opium from India to China. She was launched in Calcutta on 12 December 1829 and ran between Calcutta and the Pearl River. In 1846 she was bought by Jardine Matheson. Designed on the lines of fast American clipper ships, the ‘Red Rover’ doubled the profits of her owners by making two voyages a year from Calcutta to China. The ship was finally lost in the early 1870s.
Opium was grown in large quantities in Bengal, and the East India Company had been granted the monopoly in trading the drug in 1773, and the right to grow it in 1793. By 1839, illegal opium sales to China were massive. In 1842, the Opium War came to an end after the signing of the Treaty of Nanking giving England control of Hong Kong. From this base of operations, opium smuggling grew with each passing year using these sleek opium clippers. Despite the early development of opium clippers in Indian and English shipbuilding yards, the British ship designers failed to adapt to the new need for speed. Their design habits had not changed from the years of the Napoleonic Wars, when the compulsory convoys had sailed at the speed of the slowest vessel.
The 'Streatham' and the opium clipper 'Red Rover'
The British East India Company was the first joint-stock corporation to be formed in England, and it eventually became one of the most powerful trading companies in the world, with a virtual monopoly on trade in India and the East Indies. The East India Company or the British East India Company and informally as John Company was an English and later British joint-stock company, which was formed to pursue trade with the East Indies but ended up trading mainly with the Indian subcontinent and Qing China. After the defeat of the Spanish Armada in 1588, London merchants presented a petition to Queen Elizabeth I for permission to sail to the Indian Ocean. Permission was granted, and on 10 April 1591 three ships sailed from Torbay around the Cape of Good Hope to the Arabian Sea. On 31 December 1600, the Queen granted a Royal Charter to "George, Earl of Cumberland, and 215 Knights, Aldermen, and Burgesses" under the name, Governor and Company of Merchants of London trading with the East Indies. The governance of the company was in the hands of one governor and 24 directors or "committees", who made up the Court of Directors. They, in turn, reported to the Court of Proprietors, which appointed them. Ten committees reported to the Court of Directors. According to tradition, business was initially transacted at the Nags Head Inn, opposite St Botolph's church in Bishopsgate, before moving to India House in Leadenhall Street. The company played a key role in the spread of British influence in India and the development of the British Empire. However, it also became involved in corruption and exploitation, and it was eventually dissolved in 1858, following the Indian Rebellion of 1857.
Set of images depicting various harbors, ports, and piers together with ships, fishing and sailing boats, and all types of haven-like places and views. All large image sets on Picryl.com are made in two steps: First, we picked a set to train AI vision to recognize the feature, and after that, we ran all 25M+ images in our database through an image recognition machine. As usual, all media in the collection belong to the public domain. There is no limitation on the dataset usage - educational, scientific, or commercial.
Tags
Date
Location
Source
Copyright info



























