Similar
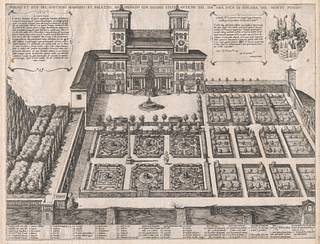
Speculum Romanae Magnificentiae: Monte Pincio Palace and Gardens
Summary
The Speculum Romanae Magnificentiae is a collection of engravings of Rome and Roman antiquities, the core of which consists of prints published by Antonio Lafreri and gathered under a title page he printed in the mid-1570's. Copies of the Speculum vary greatly in the number of prints, and individual prints were reissued and changed over time.
In 1540 Antonio Lafreri, a native of Besançon transplanted to Rome, began publishing maps and other printed images that depicted major monuments and antiquities in Rome. These images were produced to appeal to the taste for classical antiquity that fueled the Renaissance. After Lafreri published a title page in the mid-1570s, collections of these prints came to be known as the Speculum Romanae Magnificentiae, the "Mirror of Roman Magnificence." Tourists and other collectors who bought prints from Lafreri made their own selections and had them individually bound. Over time, Lafreri's title page served as starting point for large and eclectic compilations, expanded and rearranged by generations of collectors.
Antonio Tempesta (1555 – 1630), was an Italian painter and engraver, whose art connects Baroque Rome and the Flemish culture of Antwerp was born in Florence. He enrolled in the Florentine Accademia delle Arti del Disegno in 1576. He was a pupil of Santi di Tito, then of the Flemish painter Joannes Stradanus. He was part of the large team of artists working under Giorgio Vasari on the interior decoration of the Palazzo Vecchio in Florence. He painted a series of turbulent and crowded battle scenes for the Medici. He also completed a series of engravings on outdoor courtly hunting scenes. When in Rome, he associated with artists from the Habsburg Netherlands. Tempesta is now best known as a printmaker in etching and engraving. He also drew many designs for tapestries.
Printmaking in woodcut and engraving came to Northern Italy within a few decades of their invention north of the Alps. Engraving probably came first to Florence in the 1440s, the goldsmith Maso Finiguerra (1426–64) used the technique. Italian engraving caught the very early Renaissance, 1460–1490. Print copying was a widely accepted practice, as well as copying of paintings viewed as images in their own right.
Tags
Date
Source
Copyright info


































