Similar
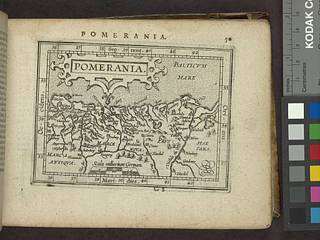
Pomerania., Abraham Ortelius - Public domain old map
Summary
Public domain image of Abraham Ortelius map, 18th century, free to use, no copyright restrictions image - Picryl description. Abraham Ortelius was a Brabantian cartographer, geographer, and cosmographer, conventionally recognized as the creator of the first modern atlas, the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum.
The first collection of maps of the world, Epitome of the Theatre of the World (1570), was produced by Mercator’s contemporary, the Belgian cartographer Abraham Ortelius. From Lawrence H. Slaughter Collection of English maps, charts, globes, books and atlases, NYPL.
In the 13th century, the Teutonic Knights, an organized Catholic medieval military order of German crusaders, conquered the Polish region of Pomerelia with Gdańsk (Danzig). For centuries, Prussia successfully expanded its size by way of an unusually well-organized and efficient army. In the 18th and 19th centuries, Prussia entered the ranks of the great powers and exercised most influence. Prussia, with its capital in Königsberg and from 1701 moved to Berlin, shaped the history of Germany. In 1871, German states united to create the German Empire. In this imperial federation, the Prussian king was also the Emperor of Germany. The term "Prussian" has often been used, especially outside of Germany, to emphasize the professionalism, aggressiveness, militarism and conservatism of the Junker class of landed aristocrats in the East who dominated first Prussia and then the German Empire. In 1918, the monarchies were abolished, and the nobility lost its political power. In the Weimar Republic, the state of Prussia lost nearly all of its legal and political importance, however, from 1918 to 1932 it was a most promising democracy in German territories. Beginning January 1945, in a period of 15 weeks, about 1,000 vessels, including Germany's largest remaining naval units, transported 900,000 refugees and 350,000 soldiers across the Baltic Sea to Germany and occupied Denmark. The MV Wilhelm Gustloff was a German military transport ship which was sunk on 30 January 1945 by Soviet submarine S-13 in the Baltic Sea while evacuating German civilians, Nazi officials, and military personnel from Gdynia (Gotenhafen) as the Red Army advanced. At least 7,000 people died, which makes it the largest loss of life in a single ship sinking in history. The Gustloff was 13 miles off the coast of Pomerania. Barely 1,100 survived. The total number of Prussian 1945’s casualties is estimated 2 to 4 million, including those who fled the Soviet army during the last months of the war before the 1945 Treaty. The Prussian population fled, mostly to the Western zones. With the end of the Nazi regime in 1945, the areas east of the Soviet Zone of Occupation, Eastern Prussia, Western Prussia, and Silesia were handed over to Poland, including Danzig, Breslau, and Stettin.
In the 17th century, maps took a huge leap forward. Mathematical and astronomical knowledge necessary to make accurate measurements had evolved. English mathematicians had perfected triangulation: navigation and surveying by right-angled triangles. Triangulation allowed navigators to set accurate courses and produced accurate land surveys. Seamen learned to correct their compasses for declination and had determined the existence of annual compass variation. Latitude determination was greatly improved with the John Davis quadrant. The measurement of distance sailed at sea was improved by another English invention, the common log. Longitudinal distance between Europe and Québec was determined by solar and lunar eclipses by the Jesuit Bressani in the 1640s and by Jean Deshayes in 1686. With accurate surveys in Europe, the grid of the modern map began to take shape.
Tags
Date
Contributors
Location
Source
Copyright info

































