Similar
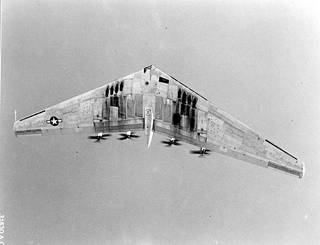
XB-35 Underneath 2 - A black and white photo of a fighter jet
Zusammenfassung
NARA B26002..23 July 46..3`630AC
Public domain photograph related to airlines, free to use, no copyright restrictions image - Picryl description
Bei den X-Flugzeugen handelt es sich um eine Reihe experimenteller US-Flugzeuge und Raketen, mit denen neue Technologien und aerodynamische Konzepte getestet und bewertet werden. Sie haben einen X-Bezeichner, der auf die Forschungsmission innerhalb des US-Systems der Flugzeugbezeichnungen hinweist. Die erste, die Bell X-1, wurde 1947 bekannt, nachdem sie als erstes Flugzeug die Schallmauer im Höhenflug durchbrochen hatte. Die meisten der X-Flugzeuge wurden vom National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) oder später von der National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) betrieben, häufig in Verbindung mit der US-Luftwaffe. Der Großteil der X-Plane-Tests fand auf dem Luftwaffenstützpunkt Edwards statt. Einige der X-Flugzeuge wurden gut publik gemacht, während andere im Geheimen entwickelt wurden. Es wird nicht erwartet, dass die meisten X-Flugzeuge in Serie gehen.
Das Album enthält Fotos von Flugzeugen der American Aviation Historical Society aus der Zeit vor und nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg.
The futuristic-looking Northrop XB-35 flying wing bomber flew for the first time in 1946 but was cancelled as soon as 1949. It was a prototype bomber aircraft that was developed in the 1940s but never entered production. The XB-35 was designed to be a long-range bomber that could carry a large payload and fly at high speeds. Jack Northrop, the founder of Northrop, had been playing with the concept of flying wings during the 1930s and 1940s and eventually produced the N-1M and N-9M designs while the proposed XP-79 fell to naught. All of this work paved the way for something grander still to come - the XB-35/YB-35 flying wing strategic bomber. The experimental Northrop YB-35, Northrop designation N-9 or NS-9, was experimental heavy bomber aircraft developed by the Northrop Corporation for the United States Army Air Forces during and shortly after World War II that later became XB-35. The USAAF ordered thirteen pre-production vehicles under the YB-35 designation on September 30th, 1943. The concept of the flying wing bomber existed before World War 2 (1939-1945). The most famous of these wartime models became the German Horten Ho 229. The major problem facing engineers was in the inherent instability of flying wings due to the technology made available at the time. The flying wing offered several key qualities that conventionally-arranged aircraft did not - more internal space meant more volume for fuel, increasing operational ranges, and there would be more storage room for internally-held ordnance. Lacking vertical tail fins, there was also less drag encountered, and the wide-area wings aided in natural lifting tendencies which reduced fuel consumption. The project was canceled due to technical challenges and the emergence of jet-powered aircraft. The XB-35 was the precursor to the B-36, which was produced in much smaller numbers and saw limited use during the Korean War.
Tags
Datum
Quelle
Copyright-info























